UTP III, our commitment
WE ARE PROUD TO BE THE OFFICIAL PARTNER OF UNDER THE POLE
By supporting Under The Pole, a pioneering underwater research expedition, we are contributing to a more sustainable world. Our support helps advance our understanding of the oceans and preserves our planet for future generations.

COMMIT TO THE FUTURE

The planet’s oceans are a pivotal natural resource: serving as climate regulators, carbon wells and halieutic resources which represent the main source of animal protein for approximately one billion people. Nonetheless, it’s estimated that we have only explored 5% of our oceans and that 90% of subsea species are yet to be discovered.
« We have better maps of the Moon, Mars, and Jupiter than we do of our own ocean floor. »
Sylvia Earle, Oceanographer and Explorer
WHAT IS THE EXPEDITION UNDER THE POLE AND WHAT DOES IT DO?
Under The Pole is a series of sub-marine expeditions whose objective is to participate in a better understanding of the underwater world by studying in particular the impact of global warming on the oceans.
Under The Pole was founded in 2010 by two dedicated adventurers who lead the venture: Ghislain Bardout – an energy systems engineer trained at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne. He also specialises in deep-sea diving in polar waters and underwater camerawork – and his wife, Emmanuelle Périé-Bardout, a skipper trained at the French national sailing academy and an expert in Polar Regions.

« The human exploration of the underwater world is a source of prodigious inspiration and an indispensable tool to uncover the mystery of the ocean. It is a powerful lever in promoting a sustainable planet. »
Ghislain Bardout, expedition director of Under The Pole
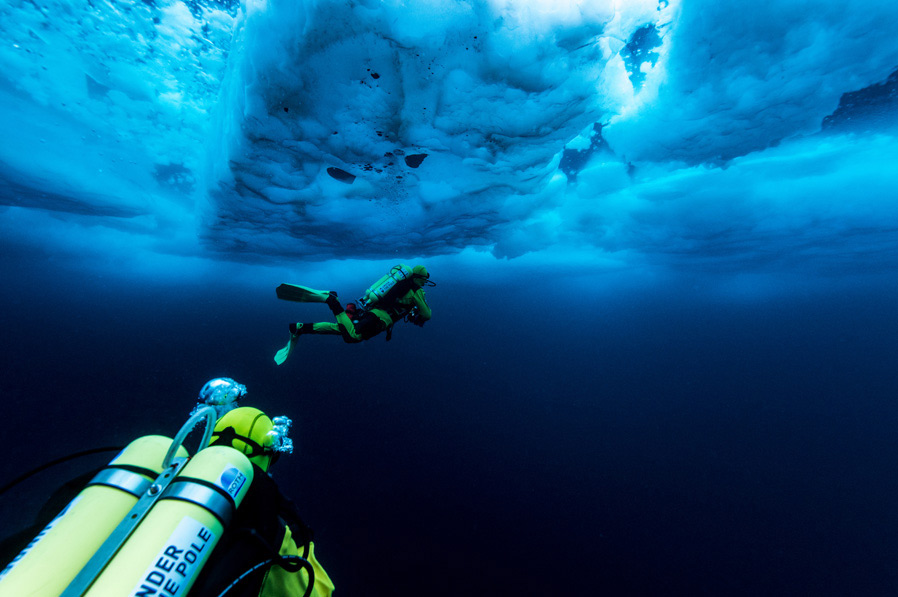
TWILIGHT ZONE
While the levels from 0 to 50 ft. deep is over explored, the mesophotic zone or Twilight Zone (50ft. to 150 ft.) remains relatively if not completely unexplored. The research will focus on the seabed of the Twilight Zone.
WHY EXPLORE THE TWILIGHT ZONE?
Exploring the twilight zone is looking to better know this resource, which is crucial to us, discovering new species and ecosystems, and better observe the scope of changes it is undergoing. This ocean layer hosts new species to discover, ecosystems to study and behaviours to understand. On average, 7 species are discovered per hour!
UNDER THE POLE’S MISSIONS
- Study the ocean and their ecosystems
- Share the discoveries with the wider public and the scientific community
- Raise public awareness to the frailty and the importance of the ecosystems with captivating pictures
- Promote the protection of the oceans

Calendrier
- January 2016 to April 2017 - The preparation of the boat at Concarneau, Brittany, France
- May 2017 - Departure towards the Arctic Ocean
- July to September 2017 - Passage through the North-West
- Autumn 2017 to Winter 2018 - Wintering of the boat at Sitka, Alaska
- Spring 2018 to Autumn 2019 - Passage through the Pacific Ocean then through to Patagonia
- Winter 2019-2020 - Navigation in the Antarctic Ocean
- Spring 2020 - The Return through the Atlantic Ocean
- June 2020 - Arrival in France
- July 2020 to December 2021 - Promotional Campaign post-expedition
SCIENTIFIC PROGRAMS
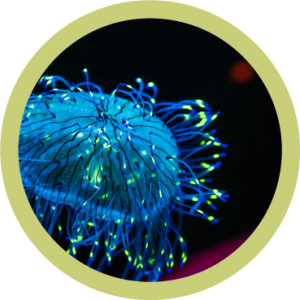
BIOLUMINESCENCE AND NATURAL FLUORESCENCE
Light plays an essential role in the ecology of numerous marine species. Some animals naturally produce it (bioluminescence), while others transmit the sunlight through other colours (natural fluorescence). These phenomena have multiple uses: communicating between species, reproduction, to protect itself against predators. Understanding how bio-fluorescence works in animals allows this knowledge to be transferred to the medical and biological field. A “natural fluorescence” built in laboratories can be used to monitor the evolution of a virus or bacteria during the infection of an animal, which may contribute to the development of antivirals or antibiotics. By marking cancerous cells, we can follow the process of metastasis and develop treatments.

DEEP CORALS OF POLYNESIA
Mostly known in warm surface waters, coral reefs have been discovered a few hundred meters deep. Overflowing with biodiversity, theses Mesophotic coral ecosystems (beyond 50 ft. below the surface) stay widely unexplored. Rarely studied, the coral ecosystems of the Twilight Zone could prove decisive in the protection of the marine heritage. Corals are subject to a lot of stress linked to anthropogenic factors and species are disappearing before we even discover them! And yet, these coral reefs bring ecosystem services of an inestimable value.

POLYNESIAN APEX PREDATORS: THE GREAT HAMMERHEAD SHARK & THE BULL SHARK
Super predators play a critical role in the balance and resilience of marine ecosystems. The main objective of this mission will be to study the ecology of two species of sharks: the great hammerhead shark and the bulldog shark. Scientific knowledge provides decision-makers with tools to make the most appropriate decisions for each region. Understanding the behaviour and role of these species will:
- better protect them (marine protected areas adapted in size and location);
- organise more sustainable ecotourism;
- raise public awareness about the protection of sharks and other super-predators.
PRACTICAL IMPLEMENTATION OF THE SCIENTIFIC PROGRAMS OF UNDER THE POLE
Science, biology, medicine and current societal challenges.
PREVIOUS EXPEDITIONS
Under The Pole I, Deepsea Under The Pole, 2010 Under The Pole II, Discovery Greenland, 2014 – 2015

WHY IS IT CRUCIAL TO PROTECT THE OCEANS?
70% of the oxygen we breathe comes from marine plants. One type of phytoplankton produces oxygen in one in five breaths. The oceans feed more than a billion men and women and they are an essential climate machine. They regulate the climate and absorb 30% of greenhouse gases.
WHY UNDER THE POLE AND BORDIER?
Exploring the oceans, becoming aware of and understanding the changes that are taking place in them means participating in a better knowledge of the world around us, with whom we interchange and interact daily. This knowledge is essential, it is indeed the first lever to make decisions and adopt responsible behaviour.
« With Under The Pole, we work for the sustainability and transmission of the assets entrusted to us. »
Michel Juvet, Bordier & Cie Partner


